As a third step to learning the Teensy LC, I decided to tackle input capture. I discovered that there is no separate interrupt vector for input capture; it is the same vector used by the timer interrupt. This means that if we are looking for a timer overflow event as well as a pin change for input capture, we must check for that specific interrupt flag within the interrupt service routine (ISR).
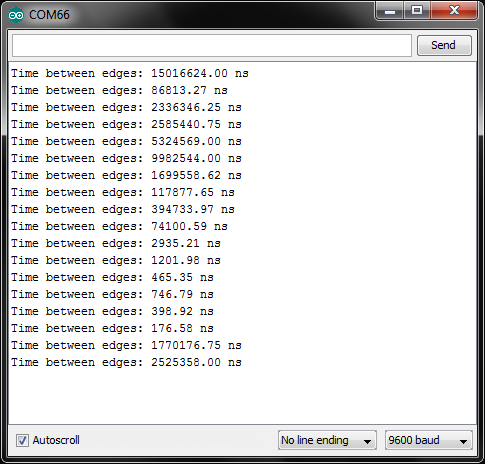
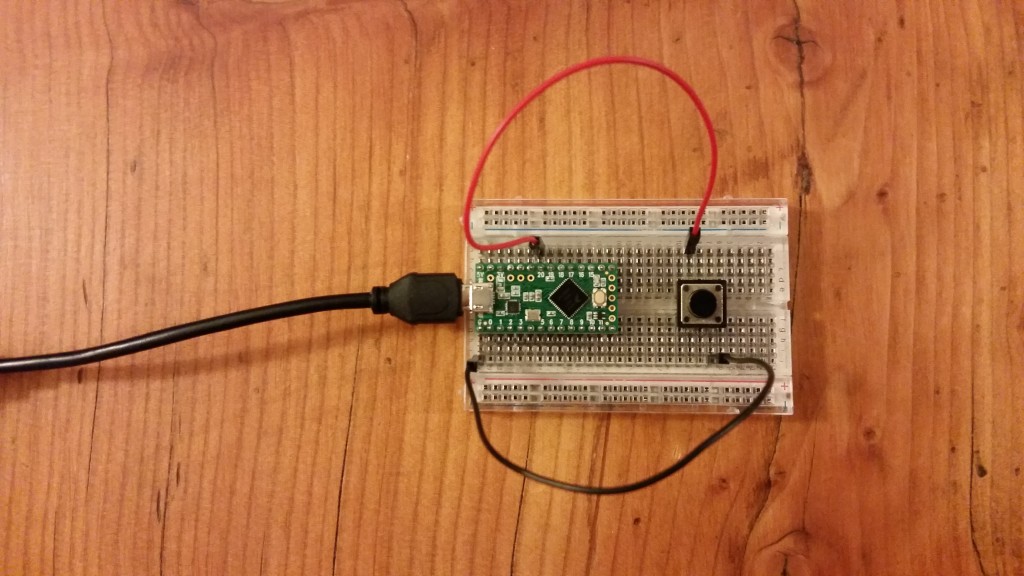
To try the example, connect a button to pin 20 of the Teensy LC, and connect the other side of the button to the Teensy LC’s ground (G) pin. Run the code and open a serial terminal. Whenever you press the button, you will see the time (in nanoseconds) between edges. Push the button a number of times, and you’ll see examples of switch bounce.
/**
* Teensy_LC_IC_Test.ino
* Shawn Hymel
* May 21, 2015
*
* Set up an interrupt service routine and input capture to
* display the time between edges of a button push. It will show
* button bounce!
*
* Pin 20 on the Teensy LC is PORT D, pin 5. It is pin 46 on the
* 48-pin QFN. This is tied to TPM0_CH5 with pin function ALT4.
*
* Connect: Teensy LC pin 16 -> Button -> Teensy LC GND
*
* Teensy LC schematic: https://www.pjrc.com/teensy/schematic.html
* MKL26Z64 datasheet: https://www.pjrc.com/teensy/KL26P121M48SF4RM.pdf
*/
volatile uint32_t count = 0;
volatile uint32_t prev_val = 0;
volatile uint32_t ovf_count = 0;
volatile uint8_t ic_flag = 0;
float gap;
void setup() {
// Set up our Serial port
Serial.begin(9600);
// The order of setting the TPMx_SC, TPMx_CNT, and TPMx_MOD
// seems to matter. You must clear _SC, set _CNT to 0, set _MOD
// to the desired value, then you can set the bit fields in _SC.
// Clear TPM0_SC register (p. 572)
FTM0_SC = 0;
// Reset the TPM0_CNT counter (p. 574)
FTM0_CNT = 0;
// Set overflow value (modulo) (p. 574)
FTM0_MOD = 0xFFFF;
// Set TPM0_SC register (p. 572)
// Bits | Va1ue | Description
// 8 | 0 | DMA: Disable DMA
// 7 | 1 | TOF: Clear Timer Overflow Flag
// 6 | 1 | TOIE: Enable Timer Overflow Interrupt
// 5 | 0 | CPWMS: TPM in up counting mode
// 4-3 | 01 | CMOD: Counter incrememnts every TPM clock
// 2-0 | 000 | PS: Prescale = 1
FTM0_SC = 0b011001000;
// Set TPM0_C5SC register (Teensy LC - pin 20) (p. 575)
// As per the note on p. 575, we must disable the channel
// first before switching channel modes. We also introduce
// a magical 1 us delay to allow the new value to take.
// Bits | Va1ue | Description
// 7 | 0 | CHF: Do nothing
// 6 | 1 | CHIE: Enable Channel Interrupt
// 5-4 | 00 | MS: Input capture
// 3-2 | 11 | ELS: Capture on rising and falling edge
// 1 | 0 | Reserved
// 0 | 0 | DMA: Disable DMA
FTM0_C5SC = 0;
delayMicroseconds(1);
FTM0_C5SC = 0b01001100;
// Set PORTD_PCR5 register (Teensy LC - pin 20) (p. 199)
// Bits | Value | Description
// 10-8 | 100 | MUX: Alt 4 attach to TPM0_CH5 (p. 179)
// 7 | 0 | Reserved
// 6 | 0 | DSE: Low drive strength
// 5 | 0 | Reserved
// 4 | 0 | PFE: Disable input filter
// 3 | 0 | Reserved
// 2 | 0 | SRE: Fast slew rate if output
// 1 | 1 | PE: Enable pull-up/down
// 0 | 1 | PS: Internal pull-up
PORTD_PCR5 = 0b10000000011;
// Nested Vector Interrupt Controller (NVIC) (p. 57)
// Also: Chapter 4.2 of the Generic User Guide
// Our FTM0 interrupt number is 17 (as per kinetis.h). We can
// use that to set up our interrupt vector and priority.
// Set the urgency of the interrupt. Lower numbers mean higher
// urgency (they will happen first). Acceptable values are
// 0, 64, 128, and 192. Default is 128. We set the priority
// (2nd byte) in the register for the FTM0 interrupt (&E000_E410)
// to 64.
NVIC_SET_PRIORITY(IRQ_FTM0, 64);
// Enable the interrupt vector. In this case, we want to execute
// the ISR (named "ftm0_isr()" for Teensy) every time TPM0
// overflows. We set bit 17 of &E000_E100.
NVIC_ENABLE_IRQ(IRQ_FTM0);
// Same as: NVIC_ISER0 |= (1 << 17);
}
void loop() {
// If an input capture event has occurred, print the time
// between edges
if ( ic_flag ) {
// Time between edges
// (1 / 48MHz) * (1 prescaler) = 20.83 ns per count
gap = count * (1 / 48.0);
Serial.print("Time between edges: ");
Serial.print(gap);
Serial.println(" ns");
// Reset input capture flag
ic_flag = 0;
}
}
// "ftm0_isr" is an interrupt vector defined for the Teensy
void ftm0_isr(void) {
uint32_t val;
// If we got to this ISR via timer overflow, we want to clear
// the timer overflow flag. We also want to count the number of
// overflows that have occurred.
if ( FTM0_SC & (1 << 7) ) {
FTM0_SC |= (1 << 7);
ovf_count++;
}
// If we got here from the input capture, we want to clear the
// channel flag.
if ( FTM0_C5SC & (1 << 7) ) {
FTM0_C5SC |= (1 << 7);
// We should only continue if we have handled the previous
// input capture
if ( !ic_flag ) {
// Retrieve the counter value and compare it to the last one.
// Take into account any overflows that have occured.
val = FTM0_C5V;
if ( ovf_count == 0 ) {
count = val - prev_val;
} else {
count = (0x10000 - prev_val) + ((ovf_count - 1) << 16) + val;
}
// Save the counter value and reset the overflow counter
prev_val = val;
ovf_count = 0;
// Set a flag so that we can read the count in the main loop
ic_flag = 1;
}
}
}