This tutorial will show you how to install TensorFlow on Windows. You do need need any special hardware. Although, you should be running Windows 10 on a 64-bit processor.
TensorFlow maintains a number of Docker images that are worth trying if you do not want to fight with version numbers. Read about how to use the TensorFlow Docker images here.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
We need to pay attention to version numbers, as TensorFlow works with only certain versions of Python. Head to this page to look at the available versions of TensorFlow.
At the time of writing, the most recent version of TensorFlow available is 2.2.0. By looking at the table, we can see that it requires Python version 3.5-3.8.
| Version | Python version | Compiler | Build tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| tensorflow-2.2.0 | 3.5-3.8 | MSVC 2019 | Bazel 2.0.0 |
Install Anaconda
While you could install TensorFlow directly on your system next to whatever Python version you wish, I recommend doing everything through Anaconda.
Anaconda provides a terminal prompt and can easily help you switch between Python environments. This proves to be extremely helpful when you want to run multiple versions of Python and TensorFlow side by side.
Head to anaconda.com and download the Individual Edition for your operating system (Windows x64). Run the Anaconda installer and accept all the default settings.
When that is complete, run the Anaconda Prompt (anaconda3).
Install TensorFlow
In the terminal, we want to create a new Python environment. This helps us keep various versions of Python and TensorFlow separate from each other (such as separate CPU and GPU versions). Enter the following commands:
conda create --name tensorflow-cpu
conda activate tensorflow-cpu
Check the version of Python that came with Anaconda using the following command:
python --version
If you want to use different version of Python, you can enter the following command (x.x is the version of Python). For example, I will install 3.7, as that falls in the acceptable version range for TensorFlow 2.2.0, which requires Python 3.5-3.8:
conda install python=x.x
If you wish to also install Jupyter Notebook, you can do so with the following:
conda install jupyter
Note that if you switch environments in Anaconda (e.g. to tensorflow-gpu), you will need to reinstall packages, as the each environment keeps everything separate.
If we run pip on its own to install TensorFlow, it will likely try to pull an outdated version. Since we want the newest release, we’ll have to tell pip where to download a specific wheel file (.whl).
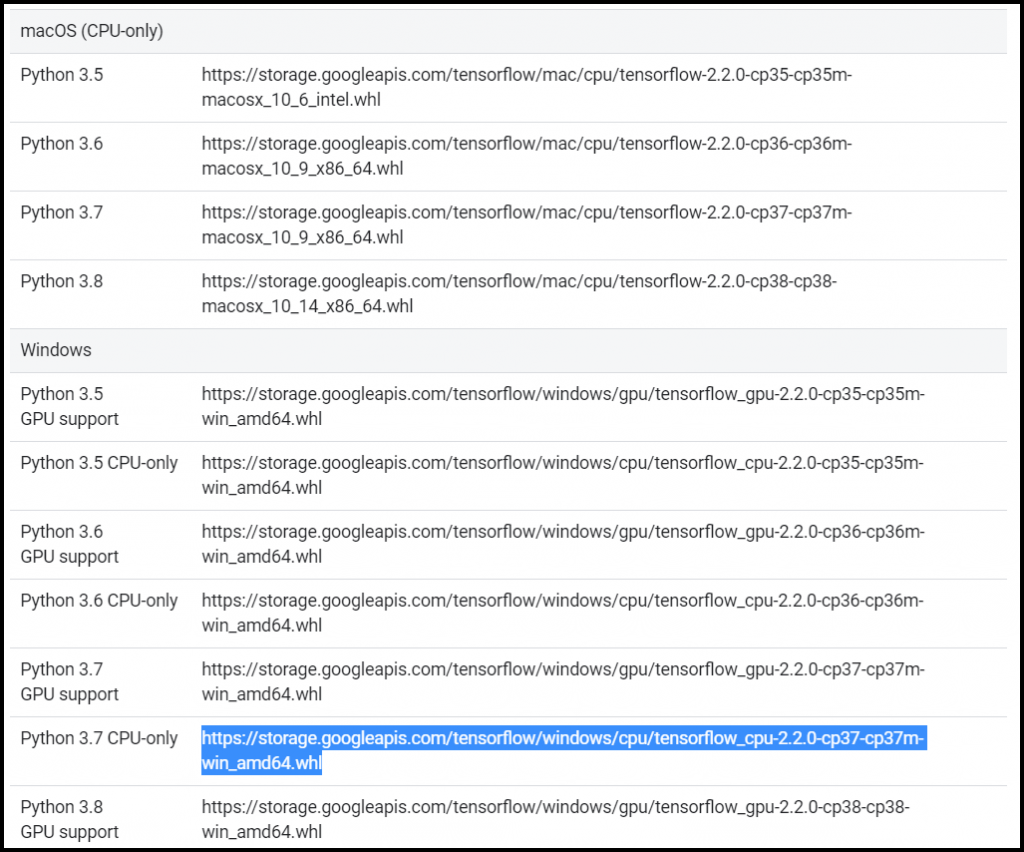
Navigate to the TensorFlow Pip Install page and look at the Package Location list.
Go to the Windows section and find the CPU-only version that supports your version of Python. For me, this will be the .whl file listed with Python 3.7 CPU-only. Note that the required versions are listed in the filename: CPU-only (_cpu), TensorFlow version (-2.2.0), and supported Python version (-cp37). Highlight and copy the .whl file URL.
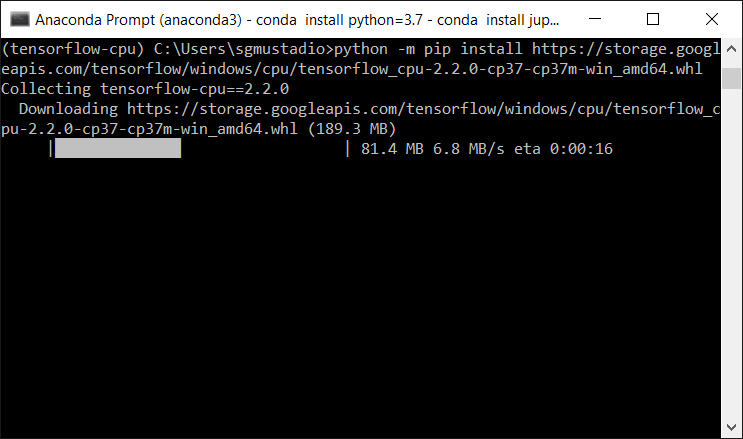
In Anaconda, enter the following command and replace <wheel_url> with the URL that you just copied:
python -m pip install <wheel_url>
Press ‘enter’ and wait a few minutes while TensorFlow installs.
When it’s done, go into the Python command line interface:
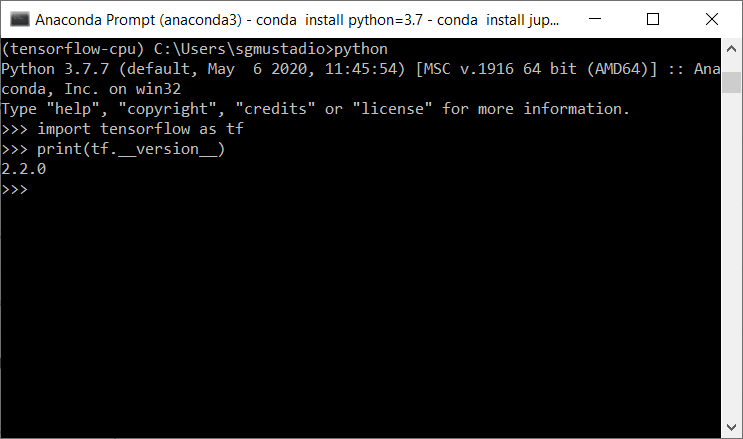
python
Check if TensorFlow is installed by entering the following commands:
import tensorflow as tf
print(tf.__version__)
You should see the version of TensorFlow printed out (e.g. “2.2.0”).
Close the Anaconda prompt.
Running TensorFlow
When you’re ready to work with TensorFlow, open the Anaconda Prompt and enter the following:
conda activate tensorflow-cpu
Now, you can use TensorFlow from within the Anaconda Prompt or start a Jupyter Notebook session.
jupyter notebook
This article gives a good introduction to using Jupyter Notebook.
If you want to install a Python package, you can do so inside of the Anaconda Prompt. Make sure that you are in the desired environment (e.g. tensorflow-cpu) first and that Jupyter Notebook is not running (quit Jupyter Notebook by pressing ctrl+c inside the Anaconda Prompt). From there, install a package with:
python -m pip install <name_of_package>
You can also install a package from inside Jupyter Notebook by running the following command in a cell:
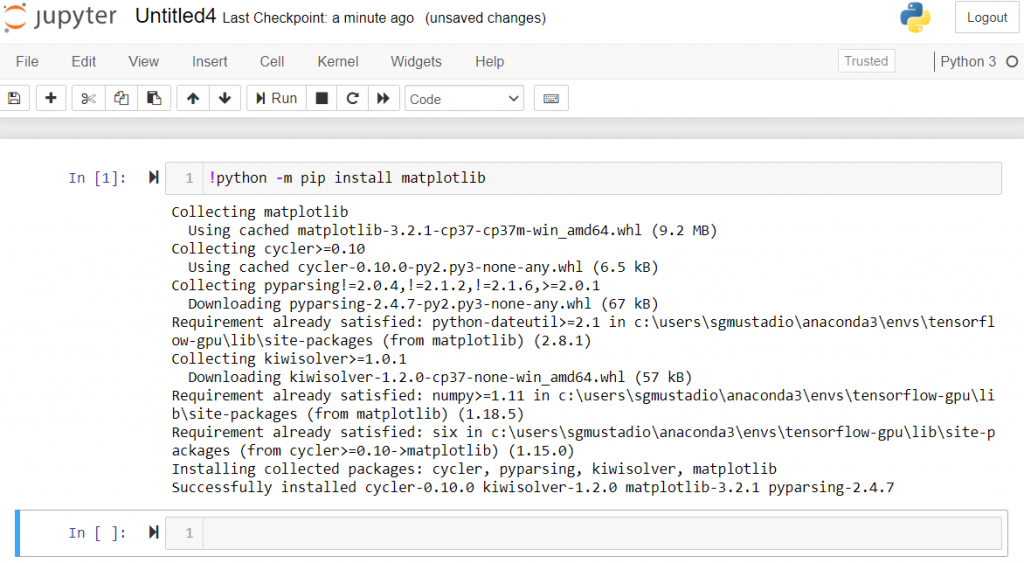
!python -m pip install <name_of_package>
For example, I installed matplotlib here:
Going Further
If you have an NVIDIA graphics card capable of running CUDA, you might be able to speed up some of your TensorFlow applications by enabling GPU support. You will need to install several drivers, and I recommend installing tensorflow-gpu in a separate Anaconda environment. See this guide on installing TensorFlow with GPU support on Windows.
See the following videos if you are looking for an introduction on TensorFlow and TensorFlow Lite:
- Getting Started with TensorFlow and Keras
- Intro to TensorFlow Lite Part 1: Wake Word Feature Extraction
- Intro to TinyML Part 1: Training a Neural Network for Arduino in TensorFlow

Hi, Thanks for this, its very easy to use and also works ! One thing to note is the TF version for windows and python 3.7.9 is now TF-CPU 2.3.0.
One question is – Why is pip used to install pachages ? Even thought pip installs TF-CPU (the whl) above, conda is the actual package manager, So is there a reason pip is being use at the end to install optional extra packages ?
Thanks for the update on the versions! Pip is the Python package manager, and conda is the package manager for Anaconda. I usually prefer pip, as that should work in any Python environment. However, conda has the added benefit of being able to install system libraries where needed, which makes things like librosa much easier to install (on Windows).